Minimally Invasive Fracture Surgery in Delhi (MIFS)
Minimally Invasive Fracture Surgery in Delhi with Dr. Neelabh focuses on small incisions, soft‑tissue preservation, precise imaging‑guided fixation, advanced pain control, and a rehab plan that helps you mobilise safely—faster.
Serving patients across Delhi & NCR (Naraina, Karol Bagh, Patel Nagar, and more)
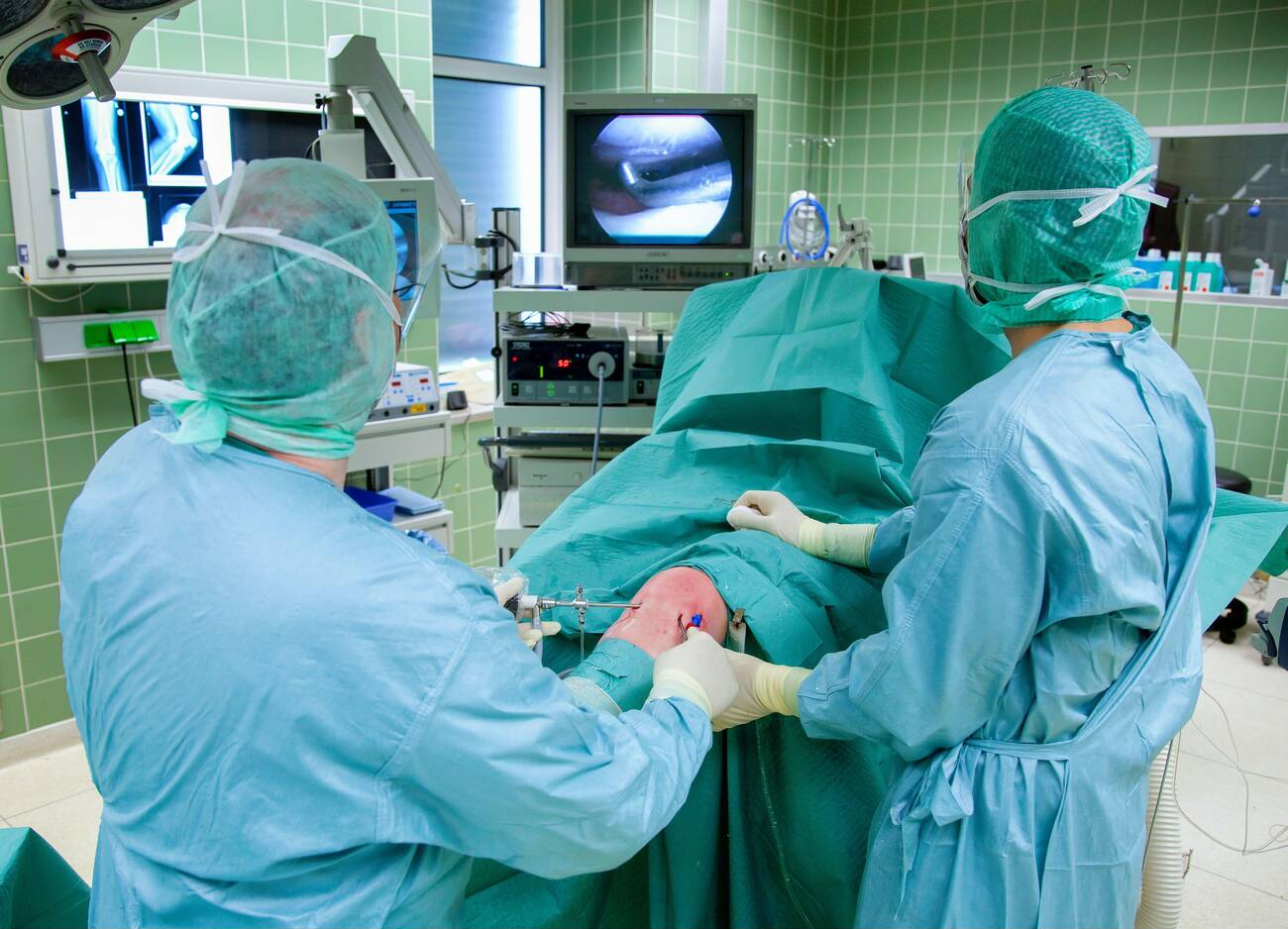
Soft‑tissue‑preserving
Small incisions and indirect reduction techniques protect blood supply and biology.
Imaging‑guided precision
Fluoroscopy‑assisted alignment and percutaneous fixation for accuracy.
Early mobilisation
Stable constructs designed to enable protected movement sooner.
Clear guidance
From first aid to full function, your pathway is mapped step‑by‑step.
What is Minimally Invasive Fracture Surgery in Delhi?
Minimally invasive fracture surgery (MIFS) uses small incisions and indirect reduction to stabilise fractures while preserving soft tissues and blood supply. Common approaches include MIPO (Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis), percutaneous screw fixation, and intramedullary nailing—often performed under real‑time X‑ray guidance.
Compared with traditional open techniques, MIFS aims to reduce surgical trauma, blood loss, infection risk, and scarring—supporting safer, earlier mobilisation when the fracture pattern allows.
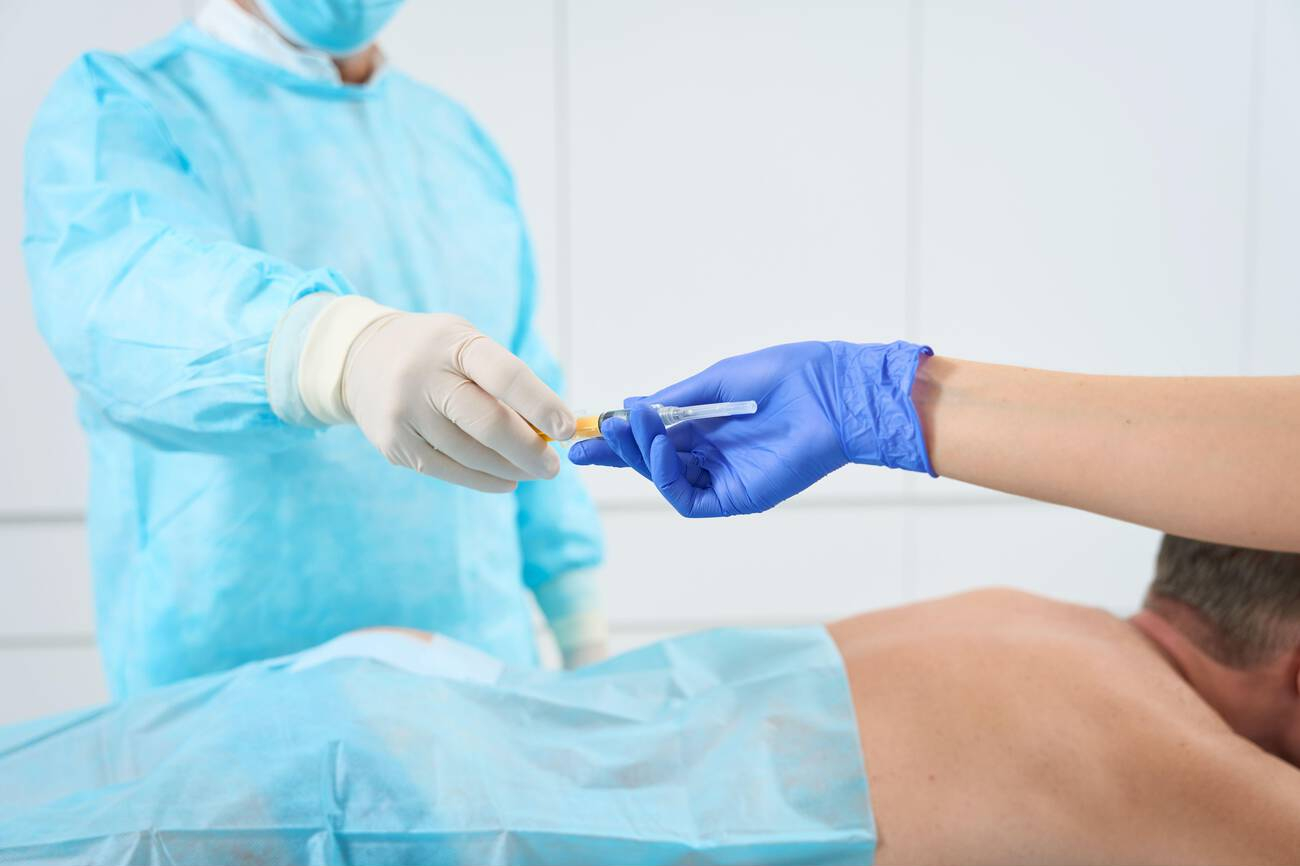
When Is MIFS Used?
Long‑bone fractures
Femur and tibia fractures suited to intramedullary nailing or bridge plating.
Peri‑articular fractures
Distal tibia, proximal tibia/plateau, distal femur, distal radius—select patterns.
Pelvis/acetabulum (select)
Percutaneous screws in carefully chosen cases.
Fragility & paediatric
Minimally invasive fixation can protect biology in osteoporotic or growing bone.
Suitability for Minimally Invasive Fracture Surgery in Delhi depends on fracture pattern, soft‑tissue status, bone quality, and your goals.
Benefits
- Smaller incisions and less soft‑tissue disruption
- Lower blood loss and potentially reduced infection risk
- Stable fixation enabling earlier, safer mobilisation
- Precise alignment with imaging guidance
Risks & How We Reduce Them
- Radiation exposure during fluoroscopy—minimised with safety protocols
- Malalignment or hardware issues—reduced with meticulous planning
- Infection, clots, stiffness, nonunion/malunion—managed with proven pathways
MIFS Techniques We Use
MIPO (bridge plating)
Through small windows, plates are slid submuscularly to bridge the fracture while preserving blood supply.
Percutaneous screws
Guidewires and cannulated screws stabilise fractures via tiny incisions.
Intramedullary nailing
Load‑sharing nails inserted through small entry points for femur/tibia fractures.
External fixation (hybrid)
Minimally invasive frames for damage‑control or definitive care in select injuries.
Arthroscopy‑assisted
Joint surface assessment and reduction for certain peri‑articular injuries.
How Surgery Is Performed
- Anaesthesia & planning: Regional or general anaesthesia; intra‑op plan confirmed with imaging.
- Closed or mini‑open reduction: Fragments aligned indirectly using traction, clamps, or joysticks.
- Fixation: Plates, screws, nails, or external fixators placed via small incisions under fluoroscopy.
- Verification: Alignment, rotation, and implant position confirmed; soft tissues protected.
- Closure & protocol: Small incisions closed; pain, wound, and mobilisation plan documented.
Weight‑bearing
Ranges from toe‑touch to early full weight‑bearing depending on fracture stability.
Infection prevention
Antibiotics, sterile technique, and clear wound‑care education.
Follow‑up
Regular reviews with X‑rays to guide rehab and activity milestones.
Recovery Timeline
- Week 0–2: Swelling control, wound care, gentle motion as advised; early muscle activation.
- Week 3–6: Gradual range‑of‑motion, isometrics, and protected use; partial weight‑bearing if permitted.
- Week 6–12: Progressive strengthening; return to desk work/light duties.
- Month 3–6+: Advance to full activities when healed radiographically and clinically.
Rehab pacing varies by injury and fixation after Minimally Invasive Fracture Surgery in Delhi.
Where to Consult Dr. Neelabh
Jeewan Hospital
Jeewan Hospital, Metro Station, 2-B, Pusa Rd, opp. Pillar No.-107, 108, Block B, Karol Bagh, New Delhi, Delhi, 110005
🕓 3:00 PM – 4:00 PM
BLK Hospital
A-4-6, Pusa Rd, Near Rajendra Place Metro Station, New Delhi-110005
🕓 4:00 PM – 6:00 PM
Clinic Intermed
Clinic Intermed, 38/16, Block 38, East Patel Nagar, Patel Nagar, New Delhi, Delhi, 110008
🕓 6:00 PM – 8:00 PM
Timings can vary on holidays and surgery days—please call +91-9810117204 to confirm.
Cost & Insurance
Costs depend on fracture pattern, implant choice, facility and anaesthesia fees, and coverage. We verify benefits and provide a transparent estimate before scheduling your Minimally Invasive Fracture Surgery in Delhi.
- Insurance pre‑authorisation & benefits check
- Clear estimate of out‑of‑pocket costs
- Cashless/financing options where applicable

How to Prepare
Medical clearance
Pre‑op evaluation, labs, ECG, and imaging as needed for safety.
Medication review
Guidance on blood thinners, diabetes medicines, and supplements.
Skin & wound care
Keep skin healthy; avoid shaving near the operative area.
Mobility aids
Arrange crutches/walker; prepare a safe home pathway.
Nutrition & habits
Stop smoking, optimise blood sugar, and prioritise protein‑rich meals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is MIFS right for every fracture?
Will small incisions heal faster?
When can I walk or use my arm?
What are the main risks?
Will the implants need removal?
Need minimally invasive fracture care?
Get a plan centred on safe healing, stability, and early mobilisation.
